Melita Internet Speed Test
Melita Internet Speed Test is an indispensable resource tailored specifically for users of Melita Internet services. This dedicated website offers a user-friendly tool designed to accurately measure internet speed, providing users with crucial insights into their connection’s performance. Unlike generic speed test tools, Melita Internet Speed Test is optimized to deliver precise results for Melita Internet subscribers, ensuring a tailored and accurate assessment of their internet speeds. Upon visiting the Melita Internet Speed Test website, users are greeted with a straightforward interface that allows for easy navigation and seamless testing. The primary function of this website is to provide users with a tool to evaluate their internet speed, enabling them to gauge the efficiency and reliability of their internet connection.
One of the key features of the Melita Internet Speed Test tool is its ability to measure internet speed in terms of Mbps (megabits per second). This unit of measurement is commonly used to quantify the rate of data transfer over an internet connection, providing users with a clear understanding of their connection’s speed capabilities. Moreover, the Melita Internet Speed Test tool goes beyond simply measuring download and upload speeds. It also provides valuable insights into other crucial metrics such as ping and jitter. Ping, also known as latency, refers to the time it takes for data to travel from the user’s device to a server and back. A lower ping indicates a more responsive internet connection, which is essential for activities such as online gaming and video conferencing. Jitter, on the other hand, measures the variability in latency over time. A stable internet connection should exhibit minimal jitter, ensuring consistent performance across different applications and tasks.
Furthermore, the Melita Internet Speed Test Tool is designed to provide accurate and reliable results by testing data multiple times and calculating an average. This approach helps eliminate inconsistencies and fluctuations that may occur during the testing process, ensuring that users receive a reasonable and representative assessment of their internet speed. In addition to these core functionalities, the Melita website may also offer additional features and resources to enhance the user experience. This may include educational materials on internet speed optimization, troubleshooting guides for common connectivity issues, and comparisons with industry benchmarks to contextualize test results.

How To Run A Speed Test: A Step-by-Step Guide
Running a speed test is a straightforward process that allows users to assess the performance of their internet connection. Whether you’re troubleshooting connectivity issues or simply curious about your internet speed, conducting a speed test can provide valuable insights into your connection’s capabilities.
This guide outlines the steps to run a speed test using the Melita Internet Speed Test tool, highlighting its features and functionalities.
Testing Melita Internet Speed With Our Website:
- Open your web browser and navigate to the Melita Internet Speed Test website.
- The website’s homepage will typically feature a prominent “Test” button to initiate the speed test.
- Click the “Test” button:
- Once you’re on the Melita Internet Speed Test website, locate the “Test” button and click on it to start the speed test.
- This action triggers the speed test tool to begin measuring your internet connection’s performance.
- Wait for the test to complete:
- After clicking the “Test” button, the speed test tool will start analyzing your internet connection.
- Depending on your internet speed and network conditions, the test may take a few seconds to complete.
- It’s essential to refrain from using the internet for other activities during the test to ensure accurate results.
Review the test results:
Once the speed test is complete, the tool will display detailed results indicating various aspects of your internet connection’s performance.
The results typically include measurements in Mbps (megabits per second), which quantify the speed of your internet connection.
Key metrics provided in the test results may include:
- Download speed: The rate at which data is transferred from the internet to your device, measured in Mbps, is most importantly discussed.
- Upload speed: The rate at which data is transferred from your device to the internet, also measured in Mbps and then is calculated and this is what its upload speed is all about.
- Ping: Ping, also known as latency, is a crucial metric in measuring the responsiveness and speed of an internet connection. It represents the time it takes for a data packet to travel from your device (such as your computer or smartphone) to a remote server and back again, typically measured in milliseconds (ms).
- Jitter: Jitter, in the context of internet connectivity, refers to the variation or inconsistency in the time it takes for data packets to travel between your device and a server over some time. It reflects the stability of your internet connection, with lower jitter values indicating a more consistent and reliable connection.
Interpret the results:
After reviewing the test results, take note of the measurements provided for download speed, upload speed, ping, and jitter.
Compare the results to your internet service provider’s advertised speeds to determine if your connection is performing as expected.
If the test results deviate significantly from your expectations or if you’re experiencing issues with your internet connection, consider troubleshooting or contacting your internet service provider for assistance.
-
Run multiple tests for accuracy:
For a more comprehensive assessment of your internet connection’s performance, consider running the speed test multiple times at different times of the day.
Running multiple tests can help identify any fluctuations or inconsistencies in your internet speed, providing a more accurate average speed measurement.
-
Understanding Internet Speed:
Internet speed is a critical aspect of online connectivity, influencing the efficiency and performance of various online activities. It refers to the rate at which data is transmitted and received over an internet connection, typically measured in megabits per second (Mbps). Understanding internet speed involves recognizing its components, including download speed, upload speed, ping, and jitter, each of which plays a significant role in determining overall internet performance.

1) Download Speed:
Download speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from the internet to the user’s device. This measurement is crucial for activities such as streaming video content, downloading files, and browsing websites. A higher download speed indicates faster data retrieval, resulting in quicker loading times for web pages and smoother streaming experiences. Download speed is often prioritized by internet users, particularly those who engage in media consumption and large file downloads.
2) Upload Speed:
Upload speed, on the other hand, pertains to the rate at which data is transferred from the user’s device to the internet. This measurement is essential for tasks such as uploading files, sending emails with attachments, and participating in online video calls or conferences. While upload speed may not be as prioritized as download speed for many users, it remains crucial for maintaining efficient communication and sharing capabilities online.
3) Ping Test:
Ping, also known as latency, measures the time it takes for data to travel from the user’s device to a server and back. It is typically measured in milliseconds (ms). A lower ping value indicates a more responsive internet connection, as it reflects shorter response times between the user’s device and the server. Ping is particularly significant for activities that require real-time interaction, such as online gaming, video conferencing, and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) calls. A stable and low ping is essential for minimizing delays and ensuring smooth, lag-free experiences in these applications.
4) Jitter:
Jitter refers to the variability or fluctuations in ping over time. It measures the stability and consistency of an internet connection, reflecting the reliability of data transmission. In other words, jitter assesses the degree of inconsistency in ping measurements, with lower jitter values indicating a more stable connection. High jitter can lead to irregularities in data delivery, resulting in disruptions and inconsistencies in online activities. While low jitter is desirable for maintaining a reliable internet connection, high jitter values may indicate underlying issues with network stability or congestion.
How Does Internet Speed Work?
Internet speed, often measured in Mbps (megabits per second), is a crucial factor in determining the performance of your online activities. Understanding how internet speed works involves delving into the intricacies of data transmission and reception over networks. This section explores the mechanics behind internet speed tests, shedding light on the technical processes that enable accurate speed measurements.
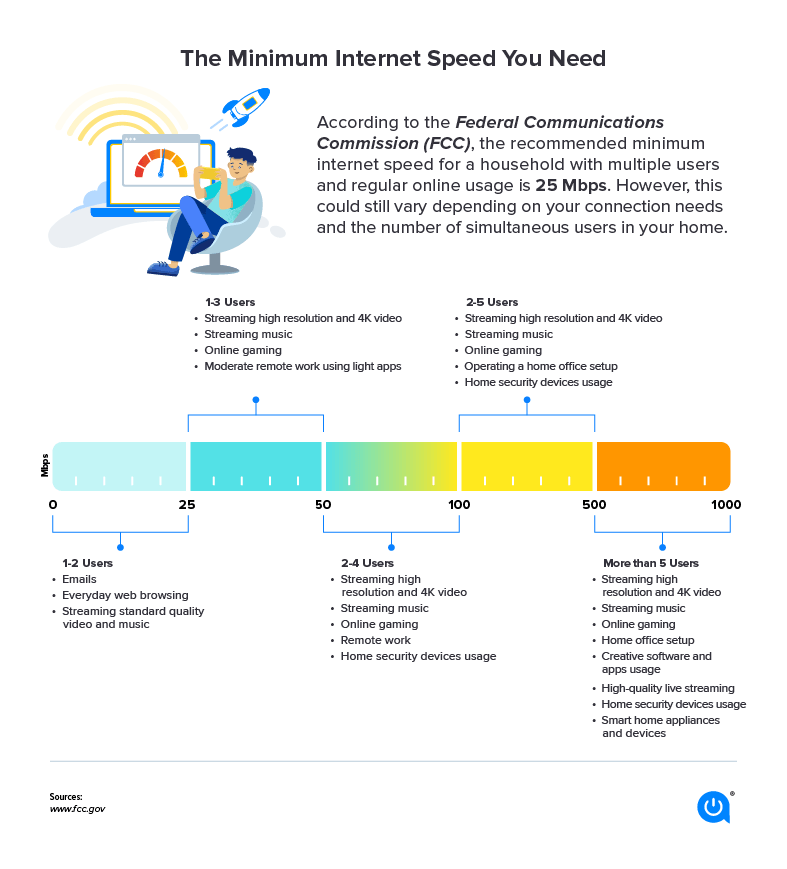
Data Transmission Basics:
Internet speed is primarily determined by the rate at which data packets travel between your device and remote servers through your internet service provider’s network. Data transmission occurs through various mediums, including cables, fibre optics, and wireless connections, with each medium offering distinct advantages and limitations.
- Transmission Mediums and Speed Variations
Different transmission mediums exhibit varying speeds and capabilities. For instance, fiber optic cables can transmit data at incredibly high speeds, making them ideal for delivering ultra-fast internet connections. On the other hand, traditional copper cables may have limitations in terms of speed and bandwidth, affecting overall internet performance.
- Internet Speed Tests:
Internet speed tests are tools designed to measure the speed and performance of your internet connection. These tests involve sending and receiving data packets between your device and remote servers, simulating real-world internet usage scenarios. By analyzing the time it takes for data to travel back and forth, speed tests provide valuable insights into your connection’s download, upload, ping, and jitter metrics.
- Measurement Metrics and Accuracy
Download speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from the internet to your device, while upload speed measures the rate of data transfer in the opposite direction. Ping, also known as latency, quantifies the time it takes for data to travel to a remote server and back, indicating the responsiveness of your connection. Jitter measures the variability in ping over time, reflecting the stability of your internet connection.
- Technical Processes:
Behind the scenes, internet speed tests employ sophisticated algorithms and protocols to accurately measure speed metrics. These tests typically involve establishing connections with multiple servers located in different geographic regions to assess performance across various network conditions. Additionally, speed tests may utilize advanced techniques such as packet loss detection and quality of service (QoS) analysis to evaluate connection stability and reliability.
- Server Selection and Load Balancing
To ensure accurate speed measurements, speed test tools often employ server selection algorithms that dynamically choose the most suitable servers based on factors such as proximity, network congestion, and server load. By distributing test requests across multiple servers, speed tests can minimize the impact of server-related variables on test results, providing more reliable speed measurements.
Troubleshooting Internet Issues
In today’s interconnected world, a reliable internet connection is essential for both personal and professional activities. However, internet connectivity issues can arise unexpectedly, disrupting our daily routines and causing frustration. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore effective troubleshooting strategies to address common internet problems and restore connectivity promptly.
1) Check the Internet Connection Between Your Router and the Computer:
When experiencing internet connectivity issues, the first step is to diagnose potential problems with the connection between your router and the computer. This involves examining both hardware and software components to identify any underlying issues.
2) Physical Connection Inspection:
Start by inspecting the physical connections between your router and computer. Ensure that all cables are securely plugged into their respective ports and that there are no visible signs of damage or wear.
If using a wired connection, check the Ethernet cable connecting your computer to the router. Consider swapping the cable with a known working one to rule out cable-related issues.
For wireless connections, verify that your computer’s Wi-Fi adapter is enabled and properly configured. Ensure that the computer is within range of the router and that there are no physical obstructions blocking the signal.
3) Restarting Devices:
Sometimes, simply restarting your router and computer can resolve connectivity issues caused by temporary glitches or software errors.
Power off your router by unplugging it from the power source, wait for a few seconds, and then plug it back in. Allow the router to boot up fully before attempting to reconnect.
Similarly, restart your computer to refresh its network settings and clear any temporary issues that may be affecting the connection.
4) Network Adapter Troubleshooting:
Check the network adapter settings on your computer to ensure they are configured correctly. Ensure that the adapter is set to obtain an IP address automatically (via DHCP) and that there are no conflicting network settings.
In Windows, you can access network adapter settings by navigating to Control Panel > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter settings. Right-click on your network adapter and select Properties to view and modify settings.
On macOS, go to System Preferences > Network, select your network connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet), and click on Advanced to access adapter settings.
5) Ensure That Your Router Is Connected to the Internet:
If your router is experiencing connectivity issues, it may be unable to establish a connection to the internet, leading to disruptions in your network access. Here are steps to ensure your router is properly connected to the internet:
6) Check the Router Status Lights:
Most routers feature status indicator lights that provide valuable information about the router’s connectivity status. Check the status lights for indicators related to internet connectivity, such as WAN (Wide Area Network) or internet status lights.
A solid or blinking WAN/internet status light typically indicates that the router is attempting to establish a connection to the internet. Refer to your router’s user manual for specific meanings of status indicator lights.
7) Verify Internet Service Provider (ISP) Status:
Contact your internet service provider (ISP) to verify if there are any known outages or service disruptions in your area. ISPs often maintain online portals or customer service hotlines to provide real-time updates on service status and outage notifications.
Alternatively, visit your ISP’s website or social media channels for announcements regarding service interruptions or maintenance schedules.
8) Check Internet Connection Settings:
Log in to your router’s web-based management interface to review and configure internet connection settings. Access the router’s management interface by entering its IP address into a web browser’s address bar.
Once logged in, navigate to the WAN or internet settings section to verify the connection type (e.g., DHCP, PPPoE) and enter any required connection details provided by your ISP. Ensure that the settings match your ISP’s requirements and that the connection is properly configured.
9) Power Cycle the Router:
Similar to restarting your computer, power cycling your router can help resolve connectivity issues caused by temporary glitches or software errors.
Power off your router by unplugging it from the power source, wait for a few seconds, and then plug it back in. Allow the router to boot up fully and attempt to reconnect to the internet.
10) Reset the Router to Factory Defaults:
As a last resort, you can reset your router to its factory default settings to restore it to a known working state. Keep in mind that this will erase any custom configurations or settings you’ve previously applied to the router.
Use a small object (such as a paperclip) to press and hold the reset button on the router for approximately 10-15 seconds. Release the reset button and wait for the router to reboot. Once reset, reconfigure the router’s settings as needed.
Conclusion
In the fast-paced digital era, a reliable internet connection is crucial for staying connected, productive, and entertained. However, encountering internet connectivity issues is not uncommon, and understanding how to troubleshoot these problems effectively can make a significant difference in restoring seamless connectivity. In this comprehensive guide, we have explored various troubleshooting strategies to address common internet issues, including problems related to router-to-computer connections and ensuring proper router internet connectivity. Troubleshooting internet issues begins with a systematic approach to identifying potential causes and diagnosing specific problems. By following a series of steps, users can effectively troubleshoot connectivity issues and implement appropriate solutions to restore reliable internet access.
Firstly, when experiencing internet connectivity issues, it’s essential to check the connection between your router and computer. This involves inspecting physical connections, such as cables and ports, and ensuring they are securely plugged in and free from damage. Additionally, restarting devices, including your router and computer, can help resolve temporary glitches or software errors that may be affecting the connection. Furthermore, verifying network adapter settings on your computer is crucial to ensuring they are configured correctly. By accessing network adapter settings and ensuring they are set to obtain an IP address automatically, users can prevent conflicts and ensure proper communication with the router.
Moreover, troubleshooting router internet connectivity issues requires several steps to ensure the router is properly connected to the internet. Users should begin by checking the status lights on the router, which provide valuable information about its connectivity status. Additionally, verifying the status of the internet service provider (ISP) and checking for any known outages or service disruptions in the area can help determine if the issue lies with the ISP.
Furthermore, reviewing and configuring internet connection settings in the router’s web-based management interface is essential for ensuring proper connectivity. Users should verify the connection type and enter any required connection details provided by the ISP to ensure the router is properly configured. If troubleshooting steps fail to resolve connectivity issues, power cycling the router or resetting it to factory defaults may be necessary as a last resort. Power cycling involves turning off the router, waiting for a few seconds, and then turning it back on to refresh its settings and establish a new connection. Resetting the router to factory defaults erases any custom configurations or settings, restoring it to a known working state.
In conclusion, troubleshooting internet issues requires a systematic approach to identifying, diagnosing, and resolving connectivity problems. By following the steps outlined in this comprehensive guide, users can effectively troubleshoot common internet issues related to router-to-computer connections and router internet connectivity. Whether resolving physical connection problems, verifying network adapter settings, or configuring router internet settings, proactive troubleshooting can help minimize downtime and ensure a seamless online experience. By implementing appropriate solutions and utilizing troubleshooting strategies, users can restore reliable internet access and enjoy uninterrupted connectivity for their personal and professional needs.
